| Principles and types of air purifiers.
Principles and Types of Air Purifiers
Only the traditional filter-based and the seemingly cooler electrostatic air purifiers can truly capture suspended particles in the air.
As for what advertisements call negative ions, ozone, ultraviolet light, plasma, activated carbon, and zeolite, their primary functions are in sterilization and adsorption of odors, but they cannot remove or filter fine suspended particles from the air.
█ Filter-Based(Sold by major brands)
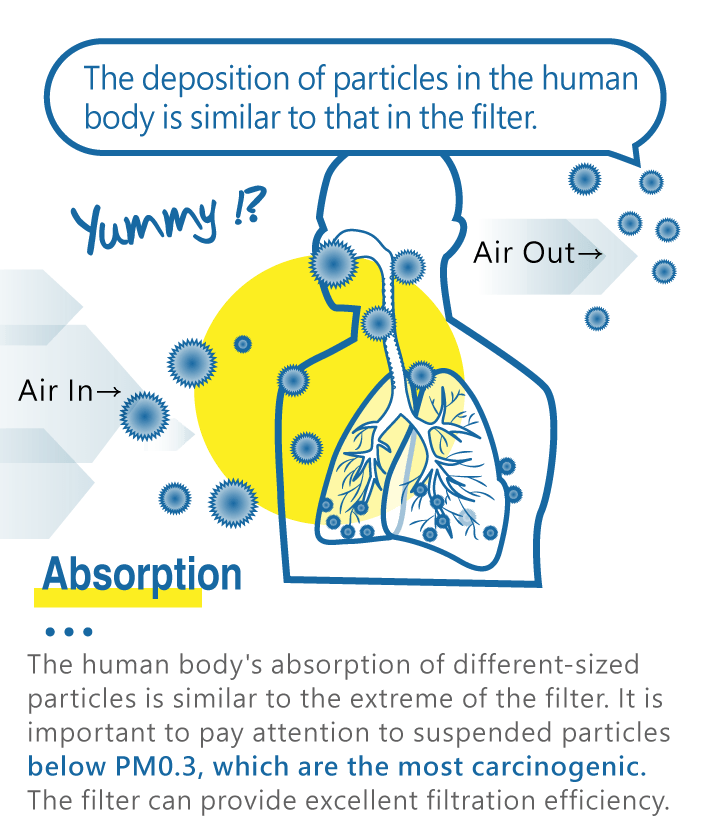
Filter-based air purifiers are the most traditional and the current form of air filtration adopted by all well-known manufacturers, even hospitals. It is the simplest and most effective way to filter suspended particles in the air and has absolutely no adverse side effects on the human body.
Moreover, the way filters capture particles of different sizes is almost identical to the way our lungs filter. It filters out particles that would otherwise settle in your lungs, effectively protecting your lung health, thus achieving a genuinely efficient air purifier.
We recommend only filter-based air purifiers without any negative ions or plasma functions to ensure zero ozone.

█ Electrostatic Air Purifiers
(Ineffective, with various issues, not sold by major brands)Electrostatic air purifiers are mainly used for industrial purposes and are another way to capture suspended particles in the air. Several key selling points for home use are 'no consumables' and 'no filter replacement.' Here's the conclusion: electrostatic air purifiers are not effective and have many drawbacks. Otherwise, why do cleanrooms in semiconductor manufacturing, operating rooms, and hospitals still insist on using traditional filter-based air purifiers?
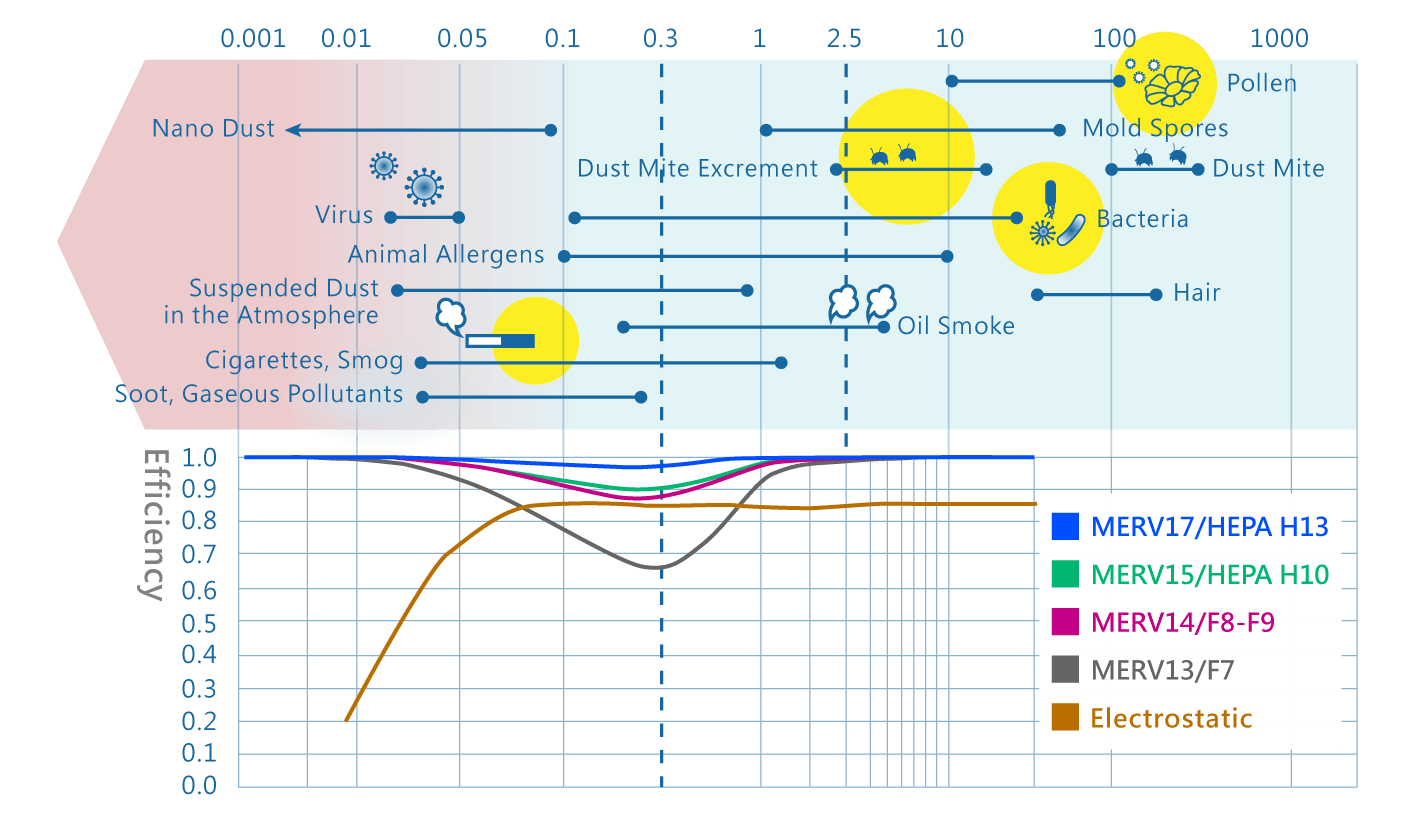
According to tests conducted by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in the United States, while electrostatic air purifiers have the most consistent filtering efficiency for particles above 0.05 microns, their overall efficiency is very poor. They perform much worse in filtering particles that cause nasal allergies (above 0.7 microns) and those below 0.03 microns than economical MERV 13 (European standard F7) filters.
In addition, electrostatic air purifiers suffer from a fatal drawback: they rapidly lose their filtering efficiency for particles smaller than 0.05 microns, which unfortunately happen to be the particles that can penetrate your bronchi and alveoli, potentially causing cancer.

Despite that home air purifiers don't typically look at filter ratings, only the final combined CADR values, electrostatic air purifiers achieve 85% filtering efficiency, even theoretically up to 99.66% after three cycles of filtration. However, electrostatic air purifiers are significantly slower at filtering the most impactful particles on human health, those larger than 1 micron and smaller than 0.01 micron. F7 filters can filter these particles efficiently in one-third of the time that electrostatic air purifiers take, while electrostatic air purifiers require three times the time and involve your lungs in helping to clean the air. Furthermore, if pollution continues to occur, electrostatic air purifiers with 85% filtering efficiency will never clean the air quickly enough. So, increasing the airflow won't enhance the effectiveness beyond a certain point.
Nevertheless, common electrostatic air purifiers in the market tend to mislead consumers who lack professional knowledge by promoting 'no filter replacement.' In reality, they are among the most expensive. To save on traditional particle filters, they introduce three more expensive consumables. The result is that they are much more expensive than the traditional filter replacement method, with the added concern of ozone generation. Electrostatic air purifiers introduce "electrode wires", "dust collection electrode plates", and "ozone adsorption screens" as additional consumables. These consumables start degrading from the day of use, typically becoming ineffective after 2-3 years, requiring replacement. As a result, electrostatic air purifiers end up being more expensive than yearly filter replacement. Electrode wires need cleaning every 1-2 weeks, as failing to do so reduces filtering efficiency, and the fine wires can be easily broken. Dust collection plates must be removed and cleaned at least once a month. If not cleaned when contaminated, they not only lose their cleaning function but also become a source of air pollution, creating more dirt. The ozone generated during electrode discharge, if not properly absorbed by the activated carbon filter, can become a source of harmful ozone, in case the filter is saturated.
Electrostatic air purifiers cause the "black wall effect" because the electrodes affect nearby furniture and objects, charging them with static electricity. This results in the air purifier unit and nearby furniture attracting dust that's hard to wipe. As for other functions, they are all additional features and cannot filter or capture fine suspended particles.
As for other functions, they are all additional and cannot filter or capture suspended particles at all.
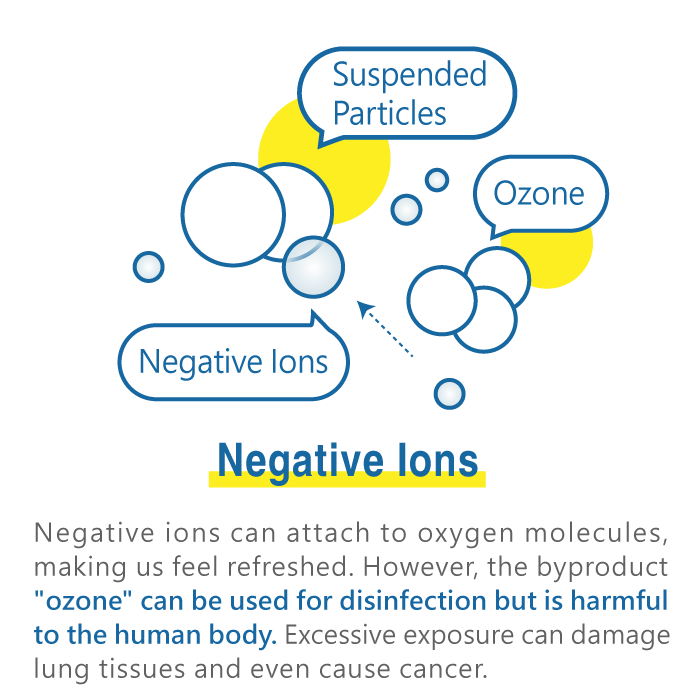
█ Negative Ions
The air is passed through a high-voltage electric field, and the machine releases electrons through an 'electron generator,' making the machine blow out electrons with a negative charge. The ability of gas molecules to capture electrons varies, with oxygen being stronger. This is how negative ions are generated through air ionization, creating a sense of freshness when inhaled. Negative ion air purifiers claim to capture suspended particles, making them heavier, accelerating their settling time, but their effectiveness is minimal, and the so-called 'negative ions' are essentially marketing jargon derived from electrostatic-related principles.
Wearable negative ion air purifiers worn around the neck are more for psychological comfort, with the effectiveness of a nomal mask, or even better filtering options available.
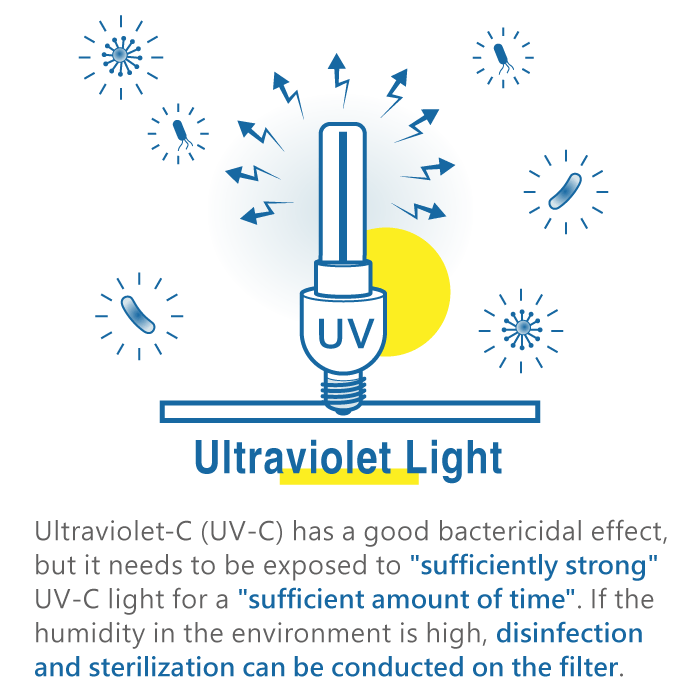
█ Ultraviolet Light
Ultraviolet-C (UVC) light has excellent sterilization effects, but to achieve sterilization, it must be exposed to "high-intensity, high-energy" ultraviolet lamps for "a considerable number of minutes." It is impossible for air purifiers to use 'high-intensity, high-energy' ultraviolet lamps, and the air passes through quickly, limiting the sterilization effect. Moreover, the majority of bacteria fall within the 0.5-10 μm range, and using just a filter method in an environment with relative humidity below 80%, microbial concentration in the air is already significantly reduced.
Unless you're setting up a cleanroom or an ICU with many patients, is it necessary to make the room sterile, lowering the body's resistance to environmental conditions?
Additionally, truly effective "high-intensity, high-energy" ultraviolet light has a significant impact on human health and generates a high amount of harmful ozone. Care should be exercised in their use.
█ Photocatalyst + UVC
Photocatalysis primarily utilizes titanium dioxide (TiO₂) to catalyze chemical reactions under the exposure of deep ultraviolet light (UVC). It harnesses the energy from a specific wavelength light source to induce catalytic reactions, exciting oxygen and water molecules in the vicinity into active free radicals. These radicals can disrupt cell membranes, leading to the loss of cell cytoplasm and resulting in the death of bacteria. Furthermore, photocatalysis can break down hydrocarbon compounds like formaldehyde into harmless water and carbon dioxide, theoretically making it a valuable supplementary.
However, similar to the situation with ultraviolet sterilization, photocatalysis also requires time to degrade organic substances. According to the research data from the Environmental Engineering Institute at National Chiao Tung University, the degradation of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) takes several seconds to several tens of seconds. If photocatalysis is used without a filter, the reaction time is insufficient, rendering it ineffective. Nonetheless, if photocatalysis is incorporated into a filter and combined with genuine sterilizing shortwave ultraviolet (UVC) light high-catalytic reactions, it can provide a dual-action reaction involving longer exposure to UVC light and the catalytic effect of photocatalysis on bacteria and viruses adhering to the filter, thus achieving effective bacterial inhibition and virus elimination.

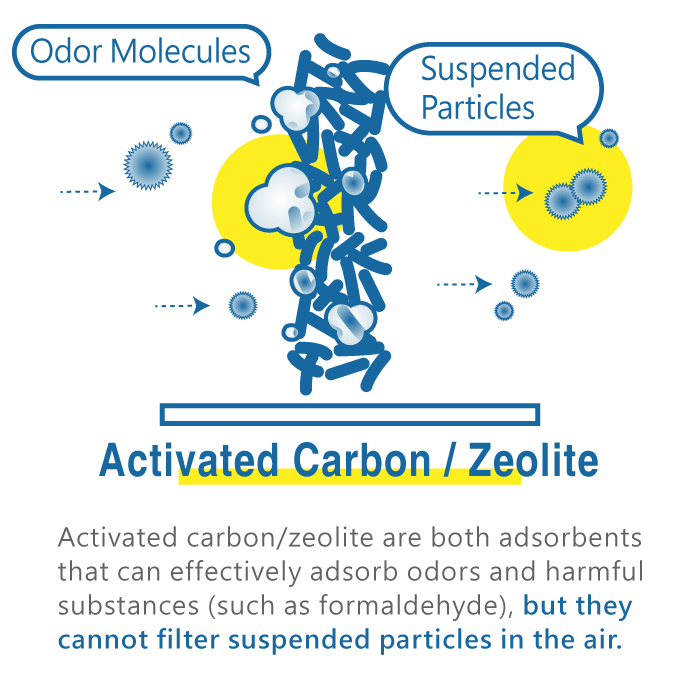
█ Activated carbon / zeolite
Activated carbon and zeolite are both adsorbents and cannot filter suspended particles in the air. However, they are effective at adsorbing odors and harmful substances (such as formaldehyde and other gaseous allergens and carcinogens). If your home is newly renovated or you've bought new furniture, using a traditional filter-based air purifier with activated carbon or zeolite filters is an excellent choice. It is effective and completely side-effect-free. The only drawback is that activated carbon and zeolite can become saturated quite easily. After opening, they might lose their effectiveness within a few weeks to several months, necessitating frequent replacement, which can be costly. It's recommended to seal unused activated carbon or zeolite to maintain their effectiveness.
| Recommended |

FLAT-LITE Manual Version
Experience the benefit of FLAT in the most economical way!
Smart Package
US$ 599

FLAT™ Wi-Fi / IoT
Perfect blends into your home decor and frees up floor space.
Smart Package
US$ 899

FLAT-BT IoT + Bt Speakers
Let your nose, eyes and ears get the best feeling at the same time.
Smart Package
US$ 999



